Unveiling the Mysteries of Volcanoes: Nature’s Powerful Creations
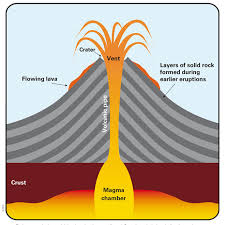
The Power and Beauty of Volcanoes
Volcanoes are some of the most awe-inspiring natural phenomena on Earth. These majestic mountains, formed by the eruption of molten rock from beneath the Earth’s crust, have both destructive and creative powers.
Volcanic eruptions can be catastrophic, causing destruction to surrounding landscapes and communities. However, they also play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface and creating new land formations. Over time, volcanic activity has contributed to the formation of islands, mountains, and even continents.
One of the most famous volcanic regions in the world is the Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped area in the Pacific Ocean known for its frequent seismic activity. This region is home to many active volcanoes that continue to shape the landscape through their eruptions.
Despite their destructive potential, volcanoes also hold a certain beauty and mystique. The sight of molten lava flowing down a mountainside or spewing into the air can be both terrifying and mesmerizing. Many people are drawn to volcanoes for their raw power and primal energy.
Scientists study volcanoes to better understand these fascinating geological features and predict their behavior. By monitoring volcanic activity, researchers can help mitigate potential hazards and protect communities living near active volcanoes.
In conclusion, volcanoes are not just mountains that spew lava – they are dynamic forces of nature that shape our planet in profound ways. Their power and beauty remind us of the Earth’s incredible diversity and resilience.
8 Positive Impacts of Volcanoes: From Land Formation to Renewable Energy
- Volcanoes create new land formations through lava flows and eruptions.
- They contribute to the Earth’s geological diversity and shape the planet’s surface.
- Volcanic eruptions release essential minerals and nutrients into the soil, enriching it for plant growth.
- Geothermal energy harnessed from volcanoes provides a sustainable source of power.
- Volcanic landscapes attract tourists and provide opportunities for adventure tourism.
- The study of volcanoes helps scientists better understand Earth’s internal processes and history.
- Volcanic ash can have beneficial effects on agriculture by enriching the soil with nutrients.
- Active volcanoes serve as natural laboratories for studying extreme environments and life forms.
Three Major Downsides of Volcanic Activity: Destruction, Disrupted Air Travel, and Constant Eruption Risk
- Volcanic eruptions can cause widespread destruction to surrounding landscapes and communities, resulting in loss of life and property.
- Volcanic ash clouds can disrupt air travel by posing a threat to aircraft engines and visibility, leading to flight cancellations and delays.
- Living near an active volcano carries the constant risk of potential eruptions, requiring residents to be prepared for evacuation at short notice.
Volcanoes create new land formations through lava flows and eruptions.
One significant benefit of volcanoes is their ability to create new land formations through lava flows and eruptions. When molten rock, ash, and gases are expelled from a volcano, they can cool and solidify to form new landmasses. Over time, these volcanic deposits can accumulate and contribute to the formation of islands, mountains, and other geological features. This process not only adds to the Earth’s land surface but also plays a crucial role in shaping the planet’s diverse landscapes.
They contribute to the Earth’s geological diversity and shape the planet’s surface.
Volcanoes play a crucial role in contributing to the Earth’s geological diversity and shaping the planet’s surface. Through their eruptions and lava flows, volcanoes create new land formations such as islands, mountains, and valleys. The constant cycle of volcanic activity helps sculpt the Earth’s landscape over time, adding to its rich tapestry of geological features. Without volcanoes, the Earth would lack the diverse topography that makes our planet unique and constantly evolving.
Volcanic eruptions release essential minerals and nutrients into the soil, enriching it for plant growth.
Volcanic eruptions play a vital role in enriching the soil with essential minerals and nutrients that are crucial for plant growth. The volcanic ash and lava contain a rich array of elements such as potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen, which act as natural fertilizers for the soil. As these minerals break down over time, they enhance the fertility of the land, promoting healthier and more robust plant growth. This natural process not only benefits local ecosystems but also provides a sustainable source of nutrients for agriculture, highlighting the invaluable contribution of volcanoes to supporting life on Earth.
Geothermal energy harnessed from volcanoes provides a sustainable source of power.
Geothermal energy harnessed from volcanoes offers a sustainable source of power that is both renewable and environmentally friendly. By tapping into the heat generated by volcanic activity deep within the Earth’s crust, we can generate electricity and heat buildings without relying on fossil fuels. This clean energy source not only reduces our carbon footprint but also helps to diversify our energy mix, making us less dependent on non-renewable resources. Harnessing geothermal energy from volcanoes presents a promising solution for transitioning towards a more sustainable and greener future.
Volcanic landscapes attract tourists and provide opportunities for adventure tourism.
Volcanic landscapes offer a unique and captivating allure that attracts tourists from around the world, providing endless opportunities for adventure tourism. From exploring rugged lava fields to witnessing active volcanic eruptions, these destinations offer thrilling experiences for those seeking excitement and exploration. Adventure seekers can hike through ancient volcanic craters, marvel at steaming geothermal vents, or even embark on helicopter tours to witness the raw power of nature up close. The dynamic and ever-changing nature of volcanic landscapes creates a sense of wonder and excitement that draws travelers looking for unforgettable experiences in some of the most awe-inspiring settings on Earth.
The study of volcanoes helps scientists better understand Earth’s internal processes and history.
The study of volcanoes provides valuable insights into Earth’s internal processes and history. By examining volcanic activity, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the planet’s composition, structure, and geological evolution. Volcanoes serve as windows into the Earth’s mantle and core, offering clues about the movement of tectonic plates, the formation of rocks, and the recycling of materials within the planet. Through studying volcanoes, researchers can unravel the mysteries of Earth’s past and present, shedding light on how our dynamic planet has evolved over millions of years.
Volcanic ash can have beneficial effects on agriculture by enriching the soil with nutrients.
Volcanic ash, despite its destructive potential during eruptions, can actually benefit agriculture by enriching the soil with nutrients. The fine particles of volcanic ash contain minerals such as potassium, phosphorus, and calcium that are essential for plant growth. When deposited on the soil surface, volcanic ash helps improve soil fertility and can enhance crop yields. Farmers in volcanic regions have long recognized the positive impact of volcanic ash on agriculture, utilizing it as a natural fertilizer to nourish their crops and promote healthy growth.
Active volcanoes serve as natural laboratories for studying extreme environments and life forms.
Active volcanoes serve as natural laboratories for studying extreme environments and life forms. The harsh conditions near volcanic vents, with high temperatures, acidic waters, and toxic gases, create a unique ecosystem that challenges traditional notions of where life can thrive. Scientists can study the resilience of microorganisms and other life forms in these extreme environments to gain insights into the origins of life on Earth and the potential for life on other planets. By exploring these volcanic environments, researchers can unlock valuable knowledge about the adaptability and diversity of life in the face of extreme conditions.
Volcanic eruptions can cause widespread destruction to surrounding landscapes and communities, resulting in loss of life and property.
Volcanic eruptions pose a significant threat to surrounding landscapes and communities, often leading to devastating consequences such as loss of life and property. The destructive power of volcanic activity can result in the destruction of homes, infrastructure, and natural habitats, displacing populations and causing long-term economic and environmental impacts. The aftermath of a volcanic eruption can be chaotic and challenging, requiring extensive recovery efforts to rebuild affected areas and support those who have been impacted by the disaster.
Volcanic ash clouds can disrupt air travel by posing a threat to aircraft engines and visibility, leading to flight cancellations and delays.
Volcanic ash clouds present a significant challenge to air travel due to their potential to disrupt flight operations. These ash clouds can pose a serious threat to aircraft engines, causing damage and even failure if the particles are ingested. Additionally, reduced visibility caused by volcanic ash can create hazardous flying conditions, leading to flight cancellations and delays as airlines prioritize passenger safety. The impact of volcanic ash on air travel highlights the need for careful monitoring and coordination between aviation authorities and volcanic monitoring agencies to ensure the safety of passengers and crew in affected regions.
Living near an active volcano carries the constant risk of potential eruptions, requiring residents to be prepared for evacuation at short notice.
Living near an active volcano poses a serious con as residents are constantly at risk of potential eruptions. The unpredictable nature of volcanic activity means that people in these areas must always be prepared for evacuation at a moment’s notice. This ongoing threat can create a sense of anxiety and uncertainty among residents, who must remain vigilant and ready to leave their homes and belongings behind to ensure their safety in the event of an eruption.
